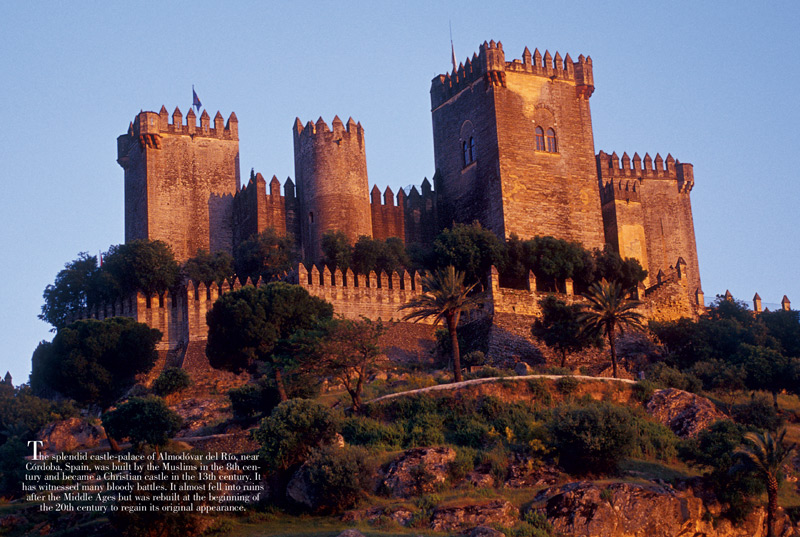



Their small, thatch-roofed, and one-roomed houses would be grouped together in an open space or on both sides of a single, narrow street. The peasants, including serfs, freeman, and villeins, on a manor lived close together in one or more villages. Servants, on the other hand, were peasants who worked in the lord's manor house, doing the cooking, cleaning, laundering, and other household chores. Sometimes a serf saved enough money to buy their freedom and become a freeman.
Serfs had small plots of land they could work for themselves. Men, women, and children worked side by side. They tended the crops, cared for the livestock, built and maintained the buildings, made the clothing, and cut firewood. Serfs did all the work on the manor farm. They were bound to the manor and could not leave it or marry without the manor lord's permission. Serfs lived in small communities called manors that were ruled by a local lord or vassal. Some peasants were freemen, who paid money or food for their land, but others, called villeins, had to work part-time for their lord. In return, the landowners protected the peasants from enemy attacks. They farmed he land of the knights, nobles, and kings. Peasants were at the bottom of the social system.

To eschew unfairness, meanness and deceit.To refrain from the wanton giving of offence.To serve the liege lord in valor and faith.
#Feudalism in the middle ages kids code#
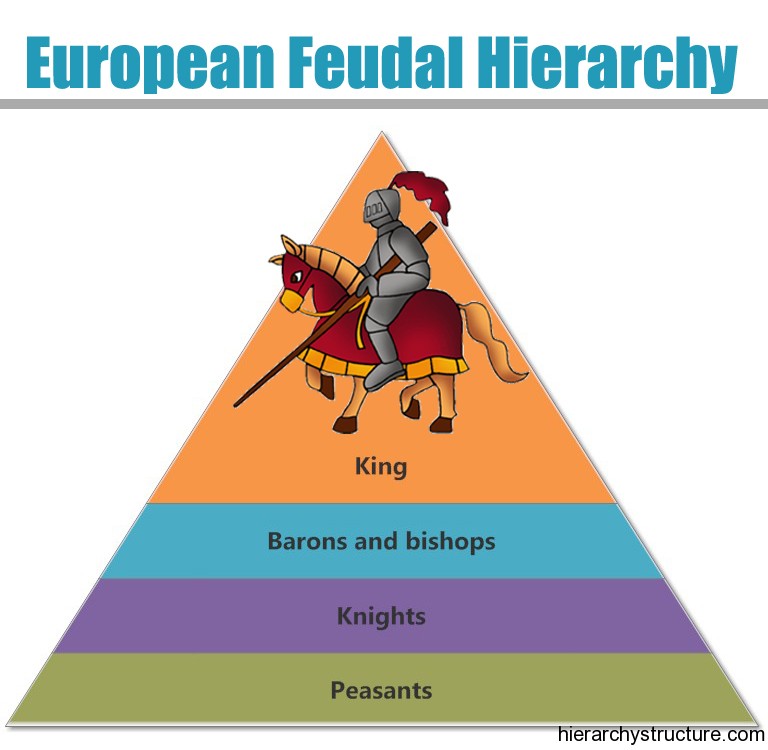
There is a code of conduct that all knights must live by. The 11th century embraced the concept of a knight as a social rank. Finally, if he proved he was a brave warrior, he was knighted by a king or noble and became a knight. Then he became a squire (squire - a knight's helper). First, he worked as a page (page - similar to a servant) who worked in the castle. Only boys from noble families could become knights. They were trained for war and fought for nobles and kings. Serfs were not much better off than slaves.Knights were considered vassals and were given land, or a fief (fief - a piece of land that is owned by a noble), by nobles as payment for their help in battle. People called serfs or peasants actually farmed the land. In return, the lords called on their knights to defend them in battle. They gave land to followers called knights. They made trouble for many rulers.ĭuring the 1000s, Europeans developed the feudal system to provide security. The Vikings came from what are now Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. However, his heirs were too weak to keep the empire-later called the Holy Roman Empire-in one piece.įrom the 800s to the 1000s, Viking invaders attacked many parts of Europe. The pope crowned Charlemagne emperor of the west in 800. He ruled the Franks in the region that is now France and Germany. The most successful king of this period was Charlemagne. Religious communities called monasteries therefore were centers of learning. Few people outside the church could read or write during the early Middle Ages. He and other church leaders became very powerful. The pope was the head of the Christian church. The church became the one thing that everyone had in common. The invaders also eventually converted to Christianity, which had become the major religion of Rome. The tribes took over the land and formed many small kingdoms. The Middle Ages began when Germanic tribes (peoples from northern Europe) invaded the western part of the Roman Empire.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
